Introduction
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, organizations aim to offer a wide range of features to users, resulting in large applications with multiple modules and pages. This complexity poses significant challenges for teams working collaboratively, especially when multiple teams need to work on a single module, page, or functionality simultaneously.
When multiple teams or developers work on the same page, it often leads to overwriting each other’s changes or conflicts during code commits. This slows down development time and necessitates repeated testing to ensure the application is error-free upon release. These challenges can significantly hinder productivity and affect the overall quality of the application.
To address these issues, one effective solution is the Micro Front-end (MFE) architecture. By adopting micro front-ends, development teams can work more independently and efficiently, reducing conflicts and improving scalability. Let’s dive into the micro front-end architecture.
What’s Micro Front-end?
Microservices on the server side represent an architectural style where an application is broken down into small, independent services that communicate over a network. Each microservice focuses on a specific business function and can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently.
Similarly, Micro Front-end architecture involves dividing a large application into smaller, more manageable front-end modules. Each module, representing a distinct feature or function of the application, can be independently built, deployed, and maintained. This modular approach enables teams to work on different parts of the application simultaneously without interfering with one another.
The primary benefits of micro front-ends include enhanced team autonomy, simplified maintenance, and improved scalability. By decomposing a large application into smaller, independent modules, organizations can achieve greater development agility and faster time-to-market for new features.
Application Design
Consider an enterprise application that includes a login page, header, side navigation, dashboard, and various features. Rather than adopting a monolithic architecture, the application can be divided into separate projects. For instance, you could create one Angular application for the login page, another for the header, and another for the side navigation, among others.
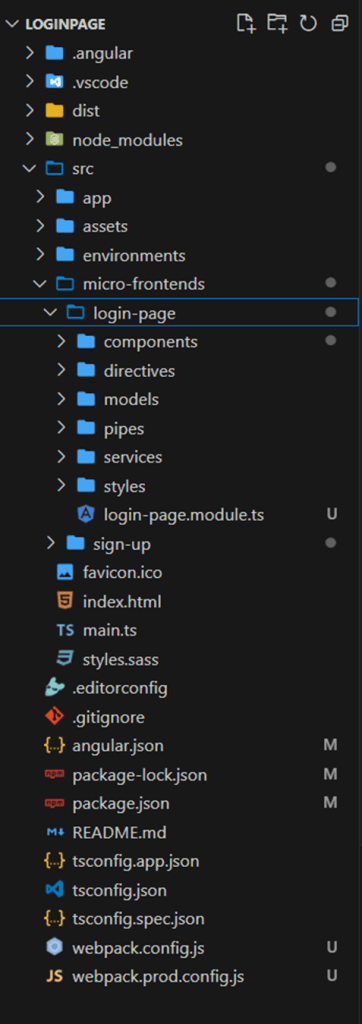
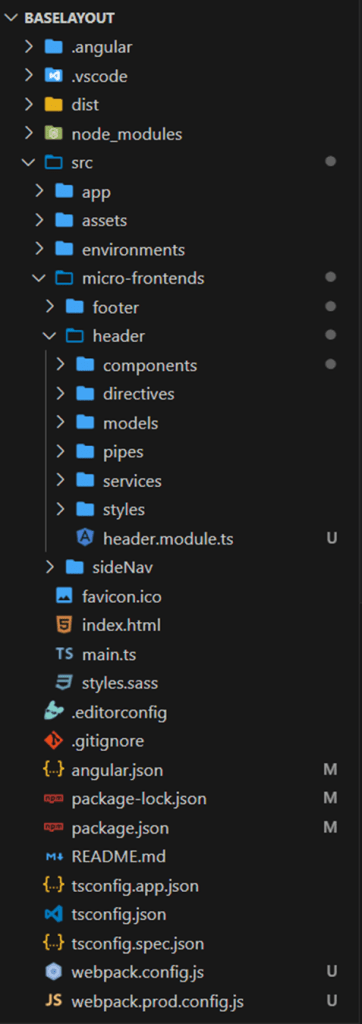
Combining Multiple Micro Front-end Projects
Combining multiple micro front-end projects into a unified application involves orchestrating and integrating them seamlessly. Here are some approaches to achieve this:
- Single-SPA Framework
Single-SPA allows you to integrate multiple JavaScript micro front-ends like Angular, React, and Vue into one application. It manages the lifecycles of each micro front-end, ensuring smooth operation.
- Webpack 5 Module Federation
Module Federation in Webpack 5 enables the sharing and loading of modules at runtime. This allows micro front-ends to be deployed independently while efficiently managing shared dependencies.
- Iframe Integration
Embedding different micro front-ends within a single host application using iframes is a simple but effective method. Communication between micro front-ends can be handled using the `postMessage` API.
- Web Components
Web components allow you to create reusable custom elements for each micro front-end. These components can be used within a host application, providing a native way to build and integrate micro front-ends.
- Micro Front-end Frameworks and Tools
Several frameworks and tools are specifically designed for micro front-end architectures, such as Bit and Luigi.
- Bit: A free open-source tool for component-driven development, allowing you to share and manage components across multiple projects.
- Luigi: An open-source micro front-end framework by SAP that helps manage navigation and communication between micro front-ends.
Detailed Example: Webpack 5 Module Federation
Module Federation in Webpack 5 allows Angular applications to share and load modules at runtime, making it an excellent tool for integrating multiple micro front-end projects. Module Federation enables code sharing between different applications without a separate build step. Each application (or micro front-end) can expose its modules and consume modules from other applications dynamically at runtime. This approach facilitates independent deployment and loading of micro front-ends, enhancing scalability and maintainability.
How It Works.
- Configuration in Webpack:
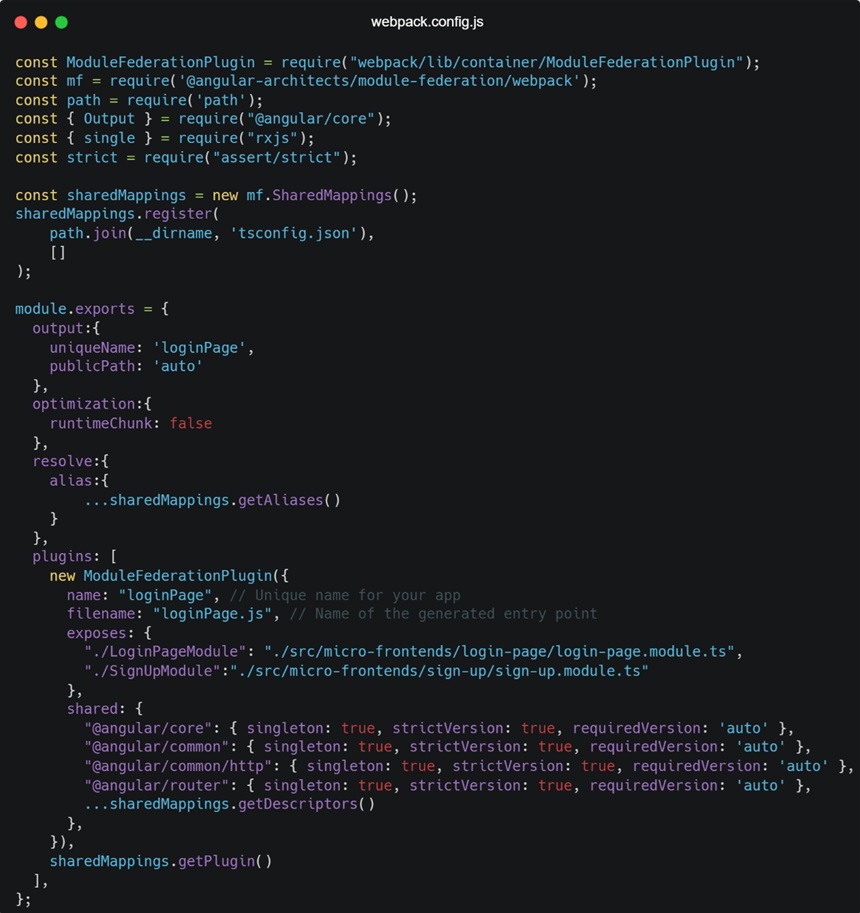
Each micro front-end’s Webpack configuration must specify which modules it exposes and which remote modules it consumes. The ModuleFederationPlugin is used to configure this in Webpack.
- Exposing Modules:
Remote applications expose their modules using the `exposes` option in the `ModuleFederationPlugin`.
- Consuming Modules:
The host application consumes remote modules using the `remotes` option in the `ModuleFederationPlugin`.
Setup
- Setting up the Remote Application
In the above micro front-end named `loginPage` that we want to expose to other applications.
- Webpack.config.js
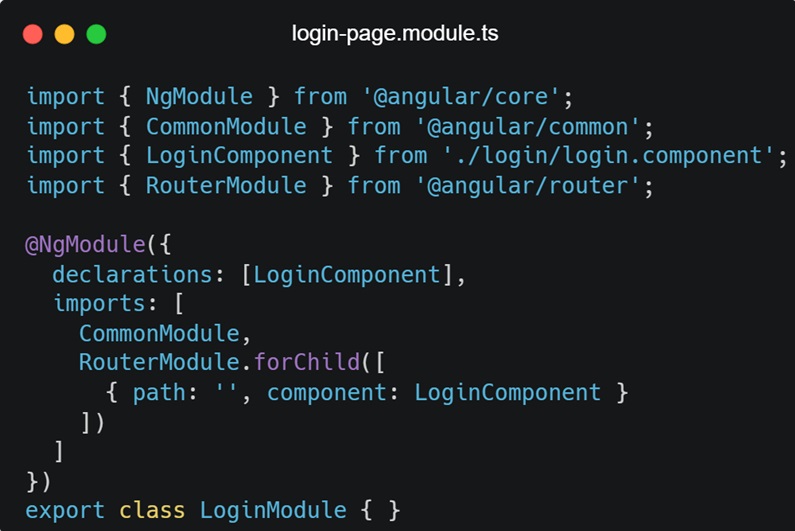
- src/app/login/login.module.ts
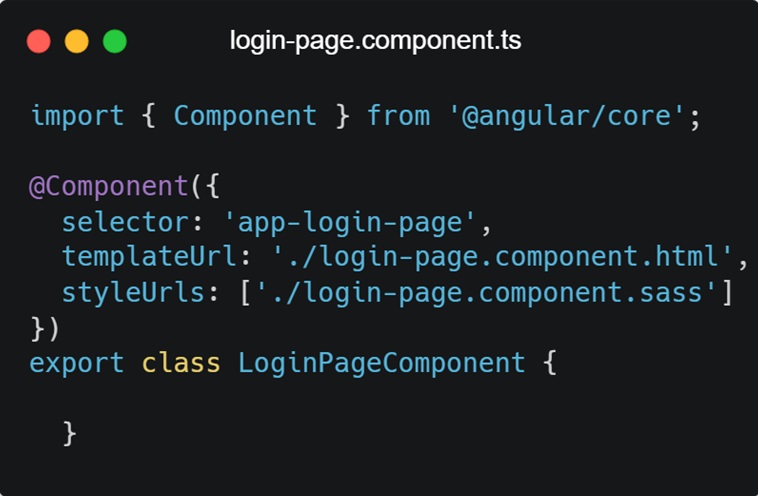
- src/app/login/login.component.ts
- Setting up the Host Application
The host application will consume the `LoginPageModule` exposed by the `loginPage` micro front-end.
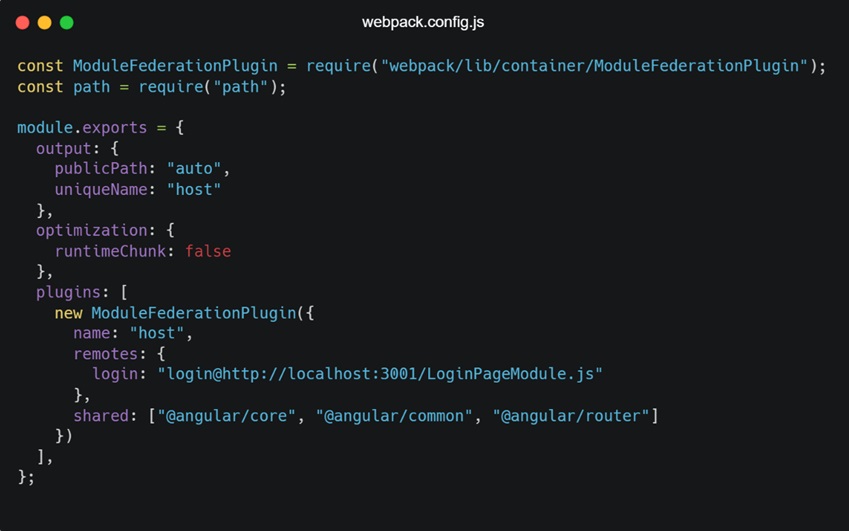
- Webpack.config.js
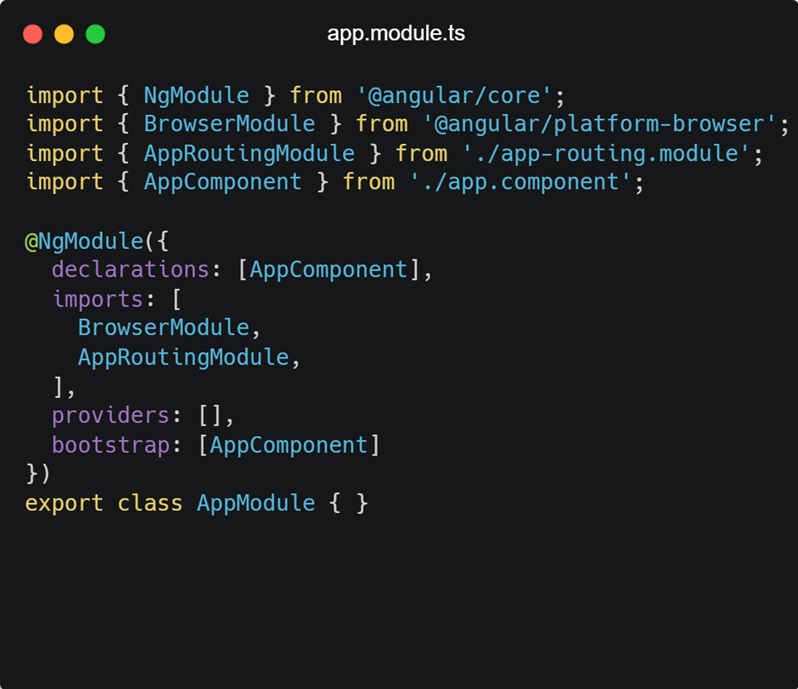
- src/app/app.module.ts
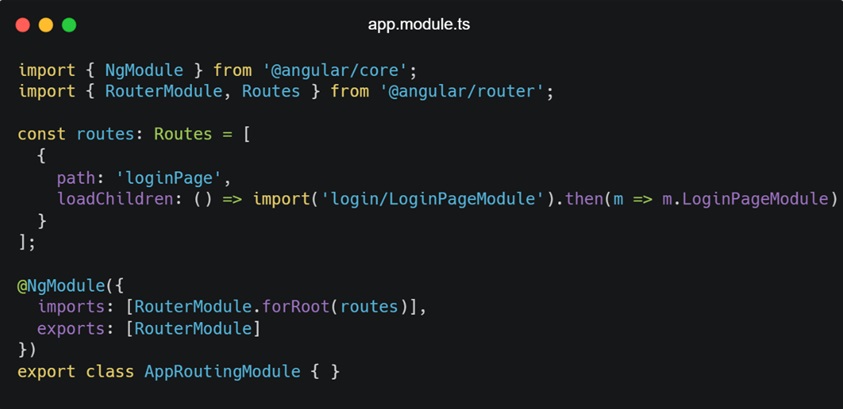
- src/app/app-routing.module.ts
- src/app/app.component.ts:

Benefits
- Independent Deployment: Each micro front-end can be deployed independently, allowing for more flexible release cycles and reduced risk.
- Shared dependencies: By sharing common dependencies, Module Federation reduces duplication and optimizes bundle sizes.
- Runtime Integration: Modules are loaded at runtime, meaning updates to one micro front-end do not require rebuilding the entire application.
- Scalability: Application can be scaled horizontally by breaking them into smaller, independently managed micro front-ends.
By adopting a micro front-end architecture and utilizing tools like Webpack 5 Module Federation, organizations can improve development efficiency, reduce conflicts, and enhance the scalability of their applications.


Leave a comment